How to Manufacture Chocolate: A Step-by-Step Process
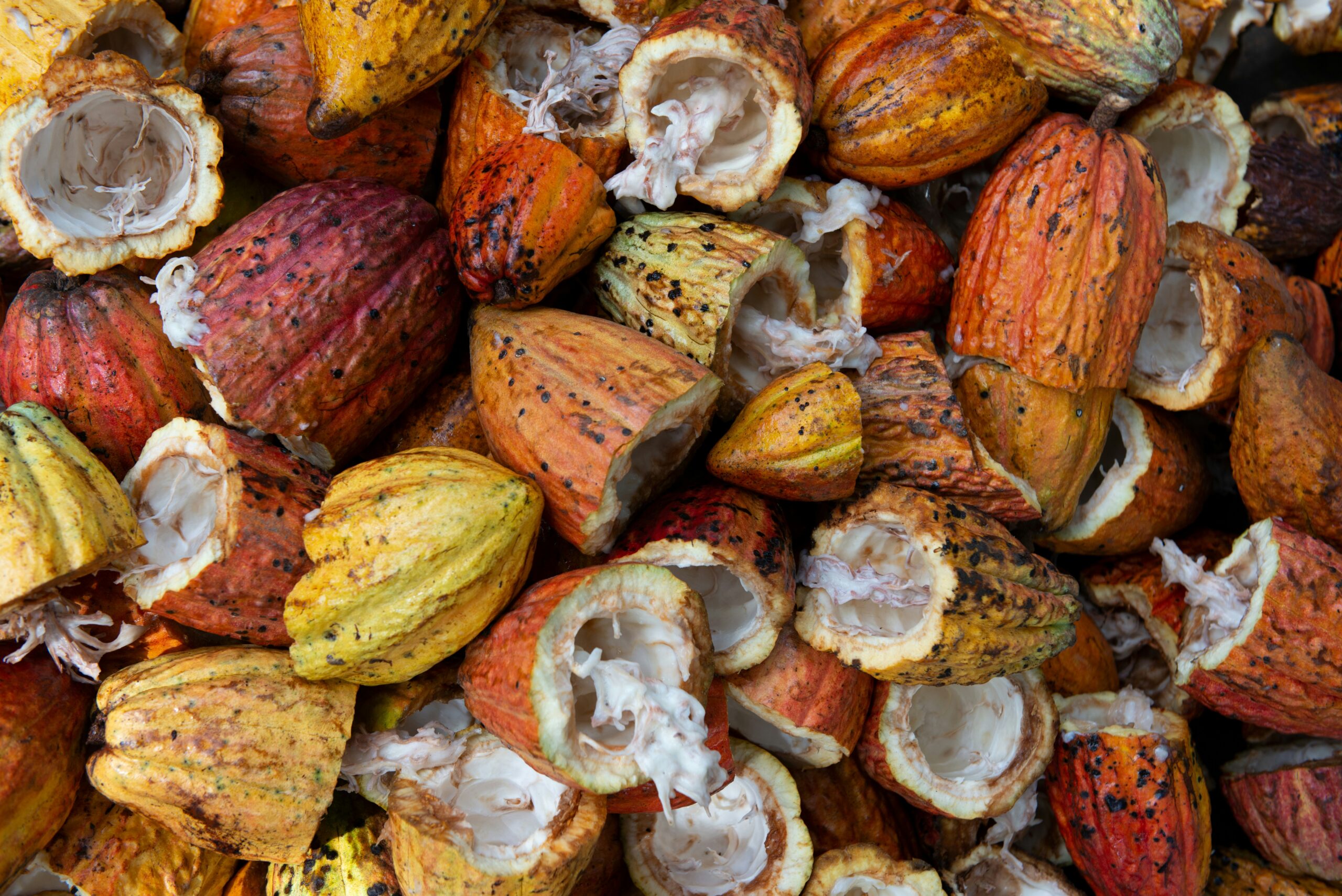
The manufacturing of chocolate is a complex and meticulous process that involves several stages, from sourcing raw materials to the final product. The primary ingredients are cocoa beans, sugar, and often milk for milk chocolate. Food manufacturers must ensure that these raw materials meet the highest quality standards, as they directly impact the taste and texture of the final product. Sourcing high-quality cocoa beans is crucial; therefore, many food business owners establish direct relationships with cocoa farmers to guarantee a steady supply of premium ingredients.
Once the cocoa beans are sourced, they undergo fermentation and drying, critical processes that enhance the beans’ flavor development. After drying, the beans are roasted, which further intensifies the flavor and aroma. The beans are then cracked and the nibs are separated, followed by a grinding process that transforms them into cocoa liquor. This liquor can be further processed to separate cocoa solids and cocoa butter, allowing chocolate manufacturers to create various chocolate products.
After obtaining the cocoa mass, the next steps involve refining and conching. Refining is used to decrease the particle size of the chocolate, enhancing its smoothness, while conching involves continuously mixing the chocolate mass under heat and aeration for several hours to develop flavor and texture. Additionally, tempering is a critical technique where the chocolate is carefully cooled and reheated to stabilize the cocoa butter crystals, ensuring a glossy finish and a satisfying snap when broken.
Quality control is paramount throughout this process. Food wholesalers and distributors must implement stringent quality checks at each stage to maintain consistency in flavor and texture. The final phase includes molding the chocolate into desired shapes, cooling, and wrapping. Different types of chocolate, such as dark, milk, and white, require specific adjustments to the manufacturing process, reflecting their unique formulations and texture profiles. By mastering these techniques, food and beverages decision-makers can ensure a successful production of high-quality chocolate, meeting consumer demands effectively.
Where to Source Quality Chocolate
When it comes to sourcing quality chocolate, food wholesalers and distributors have several options to consider. One of the most reliable methods is to procure chocolate directly from manufacturers. This approach allows for direct communication regarding product specifications, quality standards, and potential customization. Additionally, dealing directly with manufacturers often ensures better pricing, as it eliminates intermediary costs associated with other sourcing methods.
Another effective procurement avenue for food business owners is to explore import options. Many countries are renowned for producing high-quality chocolate, and importing these products can offer unique flavors and formulations not available locally. It is essential, however, for food manufacturers and distributors to ensure that they comply with local regulations and standards when importing food products, as each region may have specific requirements that must be fulfilled.
Wholesalers can also consider established wholesale suppliers that specialize in chocolate products. Many of these suppliers offer a wide range of chocolates from different manufacturers, enabling food and beverages decision makers to diversify their product offerings. When choosing a wholesale supplier, factors such as certifications, transparency in sourcing practices, and the breadth of product range should be carefully evaluated. Certifications that indicate ethical sourcing practices, such as Fair Trade or Rainforest Alliance, can be particularly important for wholesalers looking to appeal to increasingly conscious consumers.
Ultimately, sourcing quality chocolate requires a keen understanding of different procurement options, an awareness of current trends in the chocolate market, and strategic partnerships with reliable suppliers. By taking these factors into consideration, food wholesalers and distributors can significantly enhance their product offerings and ensure customer satisfaction.
The History of Chocolate: Discovering Its Origins
Chocolate, a beloved indulgence today, has a rich and complex history that dates back to ancient civilizations. The origins of chocolate can be traced to Mesoamerican cultures, where the cacao bean was revered not only for its taste but also for its significance in rituals and trade. The Olmecs, one of the earliest known civilizations to cultivate cacao, utilized the beans around 1500 BCE, making them one of the first food manufacturers to recognize cacao’s value. They prepared a frothy beverage called “xocoatl,” which was consumed during special occasions and as a ceremonial drink.
As time progressed, the Mayans and Aztecs embraced cacao, elevating it to a status symbol. For the Aztecs, cacao beans were so precious that they were used as currency, exemplifying the importance of this food commodity in their economy. When Spanish conquistadors arrived in the early 16th century, they encountered this cultural treasure and soon introduced chocolate to Europe, transforming it from a traditional beverage into a symbol of luxury. The introduction of sugar to the bitter cacao concoction made it widely appealing to the European palate, resulting in a burgeoning chocolate market.
The evolution of chocolate continued with significant innovations in production techniques during the Industrial Revolution, leading to the establishment of large-scale chocolate manufacturing. This period saw the introduction of methods such as conching and tempering, which enhanced the texture and flavor of chocolate products. As chocolate manufacturing progressed, food business owners and food wholesalers began to take notice of different types of chocolate, from dark to milk varieties, catering to a net of diverse consumer preferences in the growing food and beverages market.
This historical journey not only highlights the transformation of chocolate but also underlines the importance of understanding its origins in contemporary chocolate production. The relationship between historical practices and modern manufacturing is vital for food manufacturers aiming to create authentic and appealing chocolate products today.
Exporting Chocolate from Turkey: Regulations and Best Practices
Exporting chocolate from Turkey involves several essential steps and adherence to specific regulations that ensure compliance and quality. First, food manufacturers and exporters must be well-versed in the necessary documentation required for successful international shipments. This includes obtaining an export license, quality certificates, and health inspections, which serve as proof that the chocolate meets both Turkish and destination country standards. Furthermore, maintaining compliance with international trade agreements is vital to prevent delays during customs clearance.
Customs regulations play a crucial role in the successful export of chocolate. Food business owners must ensure that they are aware of tariff classifications and any quotas that may apply to their specific products. Engaging with a qualified customs broker can streamline the exporting process by providing the necessary guidance and ensuring that all paperwork is accurately completed and submitted on time. This partnership can significantly reduce the risk of incurring additional costs or fines due to regulatory non-compliance.
Quality preservation during transport is another pivotal aspect of chocolate exporting. Since chocolate is sensitive to temperature variations, it is imperative to use cooled containers equipped with temperature controls. This prevents the chocolate from melting or developing an undesirable texture. Additionally, ensuring proper packaging will mitigate the risk of damage during transit. Packaging designed specifically for chocolate can influence its shelf life and overall quality, which is crucial, especially for food and beverage decision makers who prioritize product integrity.
In conclusion, understanding the procedures, regulations, and best practices for exporting chocolate from Turkey is essential for food wholesalers and distributors aiming to expand their reach in international markets. By adhering to proper documentation requirements and utilizing appropriate transportation methods, businesses can enhance their overall operational efficiency and customer satisfaction.